
Therefore, two LED luminaires with the same wattage can have different brightness. Each component has an influence on the energy efficiency of the lamp. The reason for this are different components within different LED lamps. This is no longer possible with LED technology. With the old light sources the brightness could be compared well on the basis of the wattage. The physical unit for the luminous flux is called lumen and is abbreviated to lm. This refers to all visible light emitted by the LED lamp in all directions. The luminous flux indicates how much light is emitted by a light source. With the Lumen Watt Calculator you can easily convert lumens into watts. In the following sections you will find the meaning and explanation of the individual terms.
In connection with brightness, the following terms are used here: Despite all its advantages, the new technology has become more complex. In the case of LED lamps, this simplified correlation no longer works. Although this is physically wrong, one had an approximate idea of how bright a 40 watt halogen spotlight or a 60 watt incandescent lamp is.

With conventional light sources, brightness was usually assumed with power input in watts.
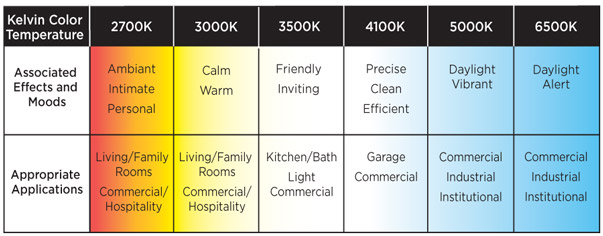
Some rooms may require extra light, but we have composed a rough guide to help. This depends on a number of factors such as room size, shape, height of ceiling and so on. So, choosing the type of bulb also helps with the number of lumens you can achieve. For example, a 15W bulb may produce 90 lumens of incandescent light, whereas an LED version can produce 135 lumens. LED bulbs usually produce the highest number of lumens with less watts compared to incandescent, halogen and CFL. The best way to look at it is to see which light bulb produces the greater number of Lumens for the smallest amount of power/wattage used. Many of the LED bulbs can produce a high lumen light output with less wattage/ power consumption than say a halogen bulb. Light bulbs get their brightness measured using something called Lumens. The cool white bulbs could work for modern day homes that need to brighten up, but these bulbs are more suited to work related rooms. The cool white bulbs can look slightly blue in colour and is perfect for kitting out warehouses to produce a clean and crisp working light. It is perfect for contemporary homes that have a fresh look, kitchens or even for office or retail lighting as it can be perfect for visual tasks due to the higher contrast than the warm white light. Neutral/natural/daylight white produces a natural light, hence the name. The warm white bulbs are perfect for living rooms for a cosy ambience, and for replacing traditional bulbs. The colour temperature for warm white differs from 1900K to 3200K and produces a similar colour to a traditional incandescent bulb. Have you wondered what colour temperature daylight is? Or possibly wanting a warm white for your living room? Let's delve into the colour temperatures available a bit more.

So, for example a 3000K bulb will emit a warm/ orange light whilst a 6000K will produce a cooler white light with a blue/white glow. The scale runs with the warmer the light colours the lower the Kelvin rating. The light colour temperature is measured in degrees Kelvin (K). The most common colour temperatures are warm white, daylight white and cool white, which are represented by degree Kelvin (K) which we shall explain further. Have you ever wondered what colour temperatures mean when looking at purchasing light bulbs? Here we explain colour temperatures and lumens and which each one means, so next time you purchase a light bulb you know exactly what specifications they mean.Ĭolour temperatures are the colour of the light that is emitted from the bulb.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
