
- Geodist dont print how to#
- Geodist dont print pdf#
- Geodist dont print driver#
- Geodist dont print code#
If you're lucky, your printer may even give you a test page with an error code or other information on it you can decipher.
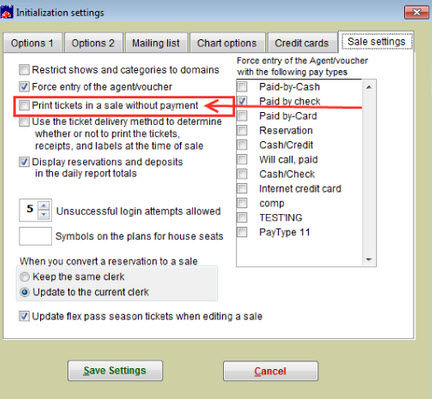
Geodist dont print driver#
If the printer can't even print its own test page, then you'll want to focus on repairing the printer rather than driver or software issues. If your printer's own test page comes out fine but Windows throws an error, you can be reasonably sure you have a software problem. Click Open Print Queue > Printer and choose Print Test Page. On a Mac, open System Preferences > Printers and Scanners, then select your printer. Select your printer, then click Manage > Print a Test Page. Windows' test pages can be printed by heading to Settings > Devices > Printers & Scanners. You can usually run your printer's self-test by pressing a series of buttons as the printer boots up, which you'll find outlined in your printer's manual. Both your printer and your computer can print test pages that may help you narrow down your issue.

If you still can't figure out the problem, it may help to run a few diagnostic tests. 4- Try printing after disabling protected view, launch Acrobat>click on Edit menu>select Preferences>click Security (Enhanced)>click Protected View>click Off>OK, relaunch Acrobat.
Geodist dont print pdf#
3- Try printing as image : Print PDF as image Adobe Acrobat, Reader.

Geodist dont print how to#
How to Set Up Two-Factor Authentication 2- Run Acrobat as an administrator - Run an Adobe program as administrator Windows 7, Vista.How to Record the Screen on Your Windows PC or Mac.How to Convert YouTube Videos to MP3 Files.How to Save Money on Your Cell Phone Bill.How to Free Up Space on Your iPhone or iPad.How to Block Robotexts and Spam Messages.Note, SNIPPET() doesn't support limiting by fields. For example, with a LIMIT 20,10 clause, SNIPPET() will be called at most 10 times. SNIPPET() is a "post limit" function, meaning that computing snippets is postponed not just until the entire final result set is ready, but even after the LIMIT clause is applied. Where myUdf() would be a UDF that fetches a document by its ID from some external storage. It can also be used to highlight the text fetched from other sources using an UDF: SELECT id, SNIPPET(myUdf(id), 'my.query', 'limit=100') FROM myIndex WHERE MATCH('my.query') SNIPPET() can also highlight non-indexed text: mysql SELECT id, SNIPPET('text to highlight', 'my.query', 'limit=100') FROM myIndex WHERE MATCH('my.query') QUERY() expression in this example returns current fulltext query. The first argument in this case should be field name: SELECT SNIPPET(body, QUERY()) FROM myIndex WHERE MATCH('my.query') Note that if you have a list of numbers from 0 to 100, LRANGE list 0 10 will return 11 elements, that is, the rightmost item is included. SNIPPET() can fetch the text to use in highlighting from the table itself. It's possible to pass options to the function as the third, fourth and so on arguments. The first two arguments are: the text to highlight, and a query. SNIPPET() can be used to highlight search results in a given text. Designing a dog waste bag holder taught me how to draw threads and articulated chains. 3d printing is a method of rapid prototyping and learning. The complete syntax and a few examples are as follows: GEODIST(lat1, lon1, lat2, lon2, ) AS dist, WEIGHT() AS w FROM test WHERE MATCH ('test') ORDER BY w DESC, dist ASC Printing cutsey things can be wasteful in the material sense, but a lot of those things lead to more useful things. GEODIST() also takes an optional 5th argument that lets you easily convert between input and output units, and pick the specific geodistance formula to use. An optimized path will be selected when one pair of the arguments refers directly to a pair attributes and the other one is constant. You can use arbitrary expression as any of the four coordinates. Note that by default both latitudes and longitudes must be in radians and the result will be in meters. GEODIST(lat1, lon1, lat2, lon2, \) function computes geosphere distance between two given points specified by their coordinates.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
